Health is a top concern among Filipinos and knowing more about diabetes is simply important. After all, it is the country’s 4th most serious disease the Philippines is identified as a hot bed because of rising cases.
Sadly, not only the Philippines, but the whole world is experiencing a diabetes crisis, and this affects both young and old alike. To complicate matters, nearly half of diabetic adults remain undiagnosed because of lack of awareness and education.
READ: What is diabetes and its four common types
Difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus (DM) has four types, but there are two most common types: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is a condition due to the lack of insulin, an important hormone produced by the pancreas to help process the sugars we intake. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune system disease where the body attacks the pancreatic cells, resulting in the cells no longer being able to produce insulin.
Type 2 diabetes on the other hand is caused by the inefficient use of insulin also known as insulin resistance. This happens when the body becomes less responsive to the presence of insulin, resulting in the rise in blood sugar levels.
The main difference between Type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that the former is a genetic condition that often shows up early in life, while the latter is mainly lifestyle-related and develops over time.
|
Type 1 Diabetes |
Type 2 Diabetes |
What is happening? |
Your body attacks the cells in your pancreas which means it cannot make any insulin. |
Your body is unable to use the insulin produced properly.
|
Risk factors |
Genetics Family history – any parent or direct sibling being diagnosed with Type 1 DM |
Family history Age Lifestyle factors such as overweight, lack of physical activity, smoking, alcohol
|
Symptoms |
Unplanned loss of weight Nausea / Vomiting Fatigue Increased thirst / urination
|
Fatigue Increased thirst / urination Yeast infections Slow healing wounds/cuts
|
Management |
Type 1 is managed mainly by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. |
Early stages of Type 2 DM may be managed with dietary intervention + exercise
Next stage will be oral anti-diabetic medications with diet control and exercise
Late stage will be the use of insulin to manage the disease
|
Cure and prevention |
Currently there is no cure for type 1 but research continues. |
Type 2 cannot be cured but it can be well managed through medication and lifestyle changes
Leading a healthy lifestyle is key to lower risks of Type 2 DM |
Risk Factors for Diabetes
There are two types of risk factors for diabetes.
Non-Controllable Risk Factors:
- Age – risk of developing diabetes increases with age especially after 40 years old
- Genetic disposition – family history of diabetes occurring in direct family members i.e. parents or siblings
Controllable Risk Factors
- Overweight – having g Body Mass Index (BMI) of 23.0kg/m2 or more
- Leading a sedentary (inactive) lifestyle
- Smoking
Diabetes can also be because of some endocrine conditions, pancreatic diseases, or drugs.
e.g., steroids
Early Signs of Diabetes
Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes share similar warning signs as follows:
Hunger and fatigue
One of the early signs for diabetes is increased hunger and fatigue, caused by insufficient insulin produced by the body. In a healthy body, food is converted into glucose that cells use for energy. If insufficient insulin is produced, they will not be able to absorb the glucose, hence resulting in these symptoms.
Frequent urination (polyuria) and extreme thirst (polydipsia)
While the average person goes to the bathroom for up to seven times in 24 hours, persons with diabetes may have to go more often. This is because the body reabsorbs glucose as it passes through your kidneys. However, as diabetes pushes the blood sugar up, the kidneys may not be able to bring it all back in - resulting in the body making more urine and having the need to consume more water, due to thirst.
Dry mouth and itchy skin
With more urine output, the body will use more fluids to produce the urine. As a result, there is less water for other body parts which may cause a feeling of dryness in the mouth and dehydration. The skin may also become dry and start to itch.
Blurred vision
As fluid levels in the body change, it could result in the lenses in your eyes swelling up. Due to the change of shape of the lenses, you may notice that your vision is sometimes out of focus.
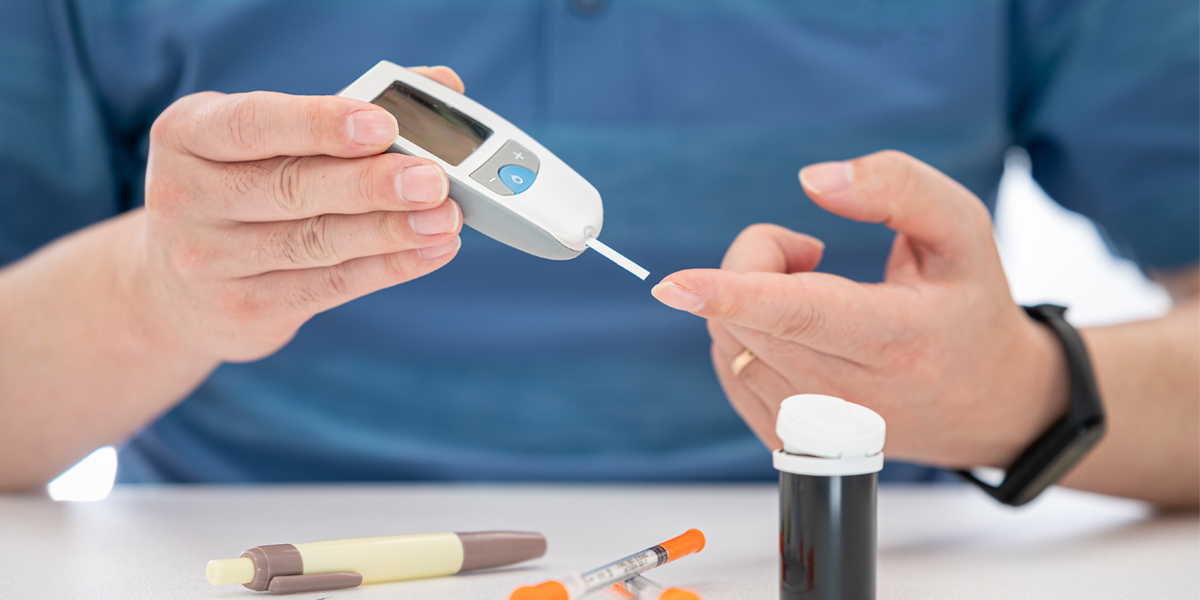
Diagnosing Diabetes
Testing your normal and fasting blood glucose levels is a straightforward indicator of the risk for diabetes.
Aside from regular diagnostic testing, building up your health funds can help ease the financial impact of getting sick. The cost of treatment remains high, even with PhilHealth or an HMO. Create your safety net with products such as SUN Fit and Well, so you can preserve your hard-earned savings and investments in case of illness. You can also ask a Sun Life Financial Advisor on the best health protection plan available for your goals and budget.






.png)

